Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
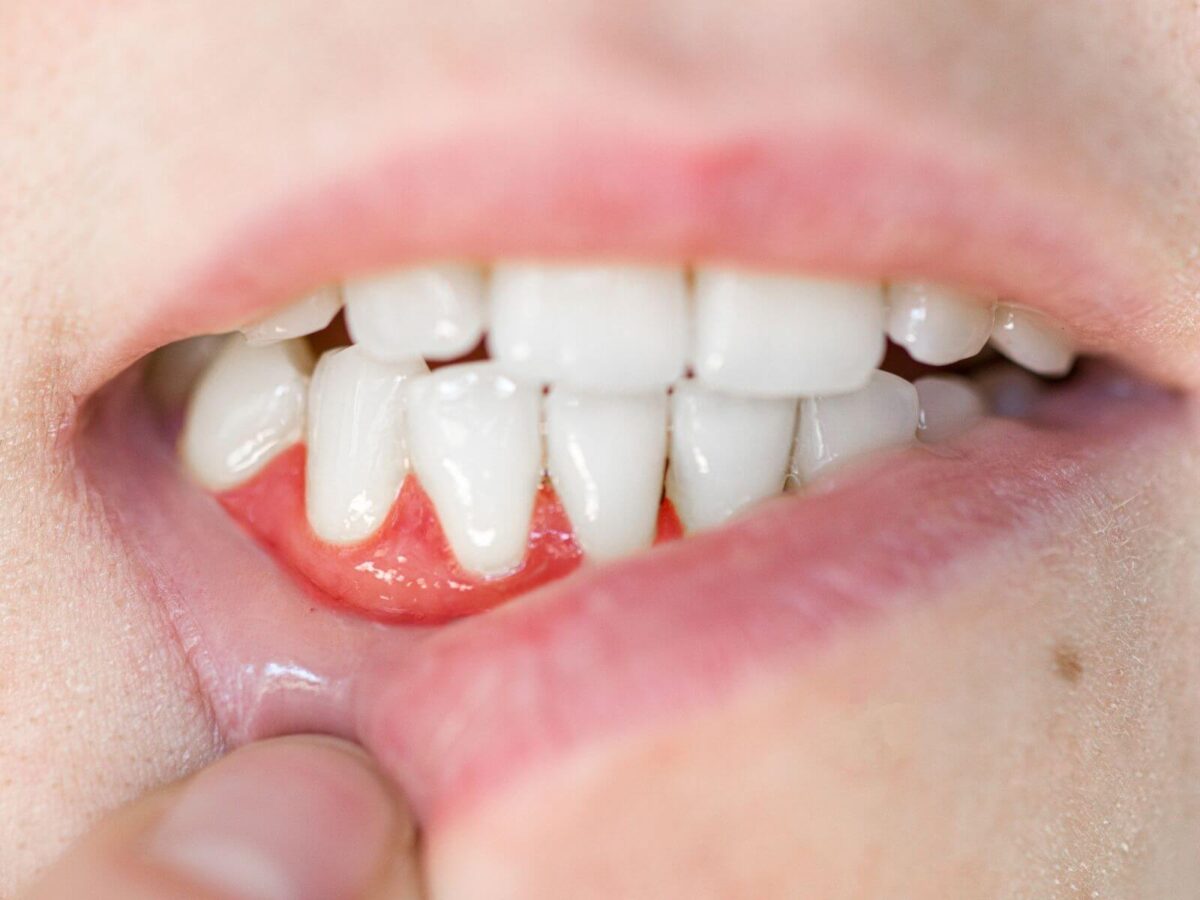
Common Causes of Gum Recession In Kids And How Parents Can Help
Gums function as the body’s most delicate tissue because they protect teeth and maintain mouth structure while teeth remain in a state of growth, which leads to gum disorders and causes severe child discomfort when left untreated.
Gum massages in babies help reduce discomfort, but milk acidity and acid erosion create tissue infection risks. Periodontal or gum disease represents children’s primary dental condition yet remains undetected throughout their growth because it stays invisible. The condition takes different forms based on age while showing intense attack behavior if patients fail to seek proper examination.
What is the Gum Recession?
Gum recession occurs whilst the tissue surrounding tooth roots retreats gradually from above or beneath the tooth surface. The sensitivity of enamel roots exceeds that of teeth, which puts enamel at risk of pain, particularly while ingesting warm, cold, acidic, or sweet meal gadgets.
Gum exposure will increase the possibility of tooth damage and tooth decay because the enamel becomes more prone to harm.
Understanding Gum Disease in Children
Although many people think that gum disease only affects adults, the reality is that children are also not protected. Young children can develop gum disease whenever they lack proper oral care routines. Gingivitis is the primary type of gum disease in children because it activates as mild gum inflammation, although it becomes severe if treatment is delayed.
The American Academy of Periodontology reports gum disease begins through gingivitis in half of the children before they become teenagers. Healthcare specialists should check patients and take steps to stop gum problems before they become severe.
Early Gum Recession Signs
Many people think gum recession is primarily a sign of aging, yet it can develop much earlier in life. Spotting gum recession at its early stage ensures prompt medical treatment. Be alert for these vital warning signs.
Sensitive Teeth
You will discover that your teeth become sensitive after the initial gum recession. The pain in sensitive tooth areas near the gumline arises because the receding gums uncover these delicate regions when eating or drinking hot, cold, or sweet items.
Visible Roots
When the roots of teeth become visible, gum recession is started. As the gums pull back, they show areas of the tooth that were hidden before the recession. The visible tooth roots modify your child’s smile appearance and exacerbate tooth sensitivity problems.
Receding Gums on Front Tooth
Receding gums first appear on the front teeth of the mouth. Your child will develop longer-looking teeth because the parts that usually hide underneath their gums start to show through. Retrocession of front tooth gums brings the highest worries as these teeth show most when smiling and affect their smile aesthetics.
Bleeding After Brushing or Flossing
When your gums bleed during or right after brushing and flossing practices, they show signs of being unhealthy. Having bleeding gums should make you visit a dentist to check for receding gums early.
Loose Teeth
When gums retreat from their natural position, they let go of teeth, which makes them move freely.
When children develop loose teeth, their gums recede, and there are signs of jawbone loss, which requires medical treatment.
Small Pockets or Gaps
The formation of little spaces between teeth and gums needs appropriate medical attention. Food particles can get stuck in the pockets and shift the bacteria to the gums, causing tooth loss.
Common Causes of Gum Recession in Kids (and What to Do About It)
Plaque and Tartar Buildup
Ongoing plaque accumulation under the gums leads to persistent inflammation, allowing extra bacteria to grow there until the gums detach from the tooth surface.
Oral care needs to be done perfectly each day to fight gum recession. Guide your child to clean all sides of their teeth and at the gumline, including areas that are challenging to access. The addition of flossing to their routine ensures the protection of gums between teeth.
Vigorous Brushing
Our message to parents is not to focus on how complex your child brushes but instead to focus on complete coverage. Watch over your child when they brush to guide brushing gently.
Demonstrate how to brush teeth softly yet completely rather than applying strong force. Stay gentle when you brush for children since their teeth require soft movements.
You should lightly stroke your child’s gum tissue instead of using intense cleaning motions.
Lip Tie
Some patients suffer gum tissue loss as an effect of lip ties. A thin band of tissue known as the frenum merges with the gumline nearby during birth. Daily force against teeth from smiling and eating actions makes the gum shrink gradually over time.
When we find a lip tie during our checkups, we suggest a procedure called frenectomy, which helps protect the gum tissues from future harm because it is painless and successful.
Parents should contact their child’s orthodontist for gum recession issues since they detect these changes during braces and recommend this step. Generally, dental braces treatments end when the recession problem disappears from the teeth.
Malocclusion (Bite is off)
The teeth of a misaligned bite handle unequal pressure when eating because they cannot correctly share force with the rest of the teeth. This repeated pressure against one tooth leads to gum damage.
A mispositioned tooth may lead to gum recession because teeth do not naturally develop at thinner gum areas. You need a professional examination to see if your teeth line up correctly through braces or another treatment plan to shield yourself from this problem.
Habits
Dental picking has become an unwanted habit among youths. Parents often miss their child picking at their gums until their dental check-up reveals oral tissue damage.
Children use different items like straws and toys to pick at their gums, while dentists discover this common habit during examinations.
When your child shows signs of gum erosion, you should discuss it with them.
How is the Gum Recession Fixed?
Oral surgery teams up with laser therapy to treat more severe cases of recession. Contact your dentist for exceptional guidance because improved home oral care did not fix the gum recession.
Look for several warning indicators to detect gum retreatment. The most straightforward sign of gum recession stands out because it shows when gum tissue moves away from the teeth, making them look longer.
Conclusion
Your child may react forcefully to dietary temperatures or experience spontaneous discomfort and gum recession symptoms. Visit your child’s dentist if they show these symptoms.
Since children do not usually share their dental problems, having them visit a dentist regularly is essential. Your child’s dentist examines for gum disease problems at regular visits regardless of what your child talks about.
We at Callen Pediatrit are here to help! We will examine your child for gum recession and suggest suitable treatment options.
It is an excellent opportunity to book your child’s next 6-month dental appointment since they have not been to the dentist recently.


